Efficacy
Actor portrayal

Actor portrayal
Two phase 2 studies showed that CRYSVITA:
- Increased and maintained serum phosphorus levels1,2
- Helped heal osteomalacia1
CRYSVITA was tested in a clinical trial program of 27 adults with TIO1
Study designs
Study 61,3
CRYSVITA was studied in a 144-week, single-arm, open-label, phase 2 study in 14 adult patients with TIO aged 33-68 years (median 59.5 years). Patients received CRYSVITA every 4 weeks at a weight-based starting dose of 0.3 mg/kg that was titrated to achieve a fasting serum phosphorus level of 2.5 to 4.0 mg/dL. The mean dose was 0.83 mg/kg at week 20, 0.87 mg/kg at week 48, 0.77 mg/kg at week 96, and 0.71 mg/kg at week 144.
No patients discontinued the study due to adverse events.
Select endpoints:
- Coprimary endpoints1,2:
- Proportion of patients achieving mean serum phosphorus levels above the lower limit of normal at the midpoint of the dosing interval, averaged across dose cycles from baseline to week 24
- Percent change from baseline to week 48 of
osteomalacia-associated bone measurements in:
- Osteoid thickness (O.Th)
- Osteoid volume/bone volume (OV/BV)
- Mineralization lag time (MLt)
- Secondary endpoint: Percent change from baseline to week 24 of serum phosphorus levels at the midpoint of the dosing interval, averaged across dose cycles1,2
- Safety: Number of subjects with adverse events (AEs) and serious adverse events (SAEs)1,3
Study 7
CRYSVITA was studied in a single-arm, open-label, phase 2 study of 13 adult patients with TIO aged 41-73 years (median 58.0 years). Patients received CRYSVITA every 4 weeks at a weight-based starting dose of 0.3 mg/kg that was titrated to achieve a fasting serum phosphorus level of 2.5 to 4.0 mg/dL. The mean (SD) dose was 0.91 (0.59) mg/kg at week 48 and 0.96 (0.70) mg/kg at week 88.1,4
No patients discontinued the study due to treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs).2,4
Select endpoints:
- Primary endpoint: Change in serum phosphate at each timepoint4
- Secondary endpoints1,4:
- Percent change from baseline to week 48 in additional histomorphometric parameters, including:
- O.Th
- OV/BV
- MLt
- Change from baseline over time in ratio of renal tubular maximum phosphorus reabsorption rate to glomerular filtration rate
- Percent change from baseline to week 48 in additional histomorphometric parameters, including:
- Safety: Number of subjects with TEAEs4
In both studies of adult patients with TIO, oral phosphate and active vitamin D analogs were discontinued 2 weeks prior to study enrollment, and were not allowed in the study.1
At baseline, patients with TIO experienced substantial disease burden
In Study 6:
- 90% of patients with known tumor location underwent attempted surgical resection2
- 45% of patients required assistance with walking2
- Time from symptom onset to diagnosis was 4.5 years on average2
In Study 7:
- 53.8% of patients had previously undergone surgery for their disease4
- The average duration of disease was 10 years4
Disease burden at baseline2,5

At baseline, histomorphometric assessments were determined in 11 out of 14 patients in Study 6 by a comparison using reference measurements. At baseline, 9 patients had osteomalacia based on histomorphometric assessments1,3:
- Mean (SD) OV/BV ratio was 21.2% (19.9), compared with a reference range of 0.3% to 3.1% in healthy postmenopausal women
- Mean (SD) O.Th was 18.9 (11.9) µm, compared with the reference range of 5.5 to 12 μm
- MLt was measurable at baseline for 3 subjects. For these 3 subjects, mean (SD) MLt was 667 (414) days, compared with a reference range of 15 to 50 days in healthy postmenopausal women
STUDIES 6 AND 7
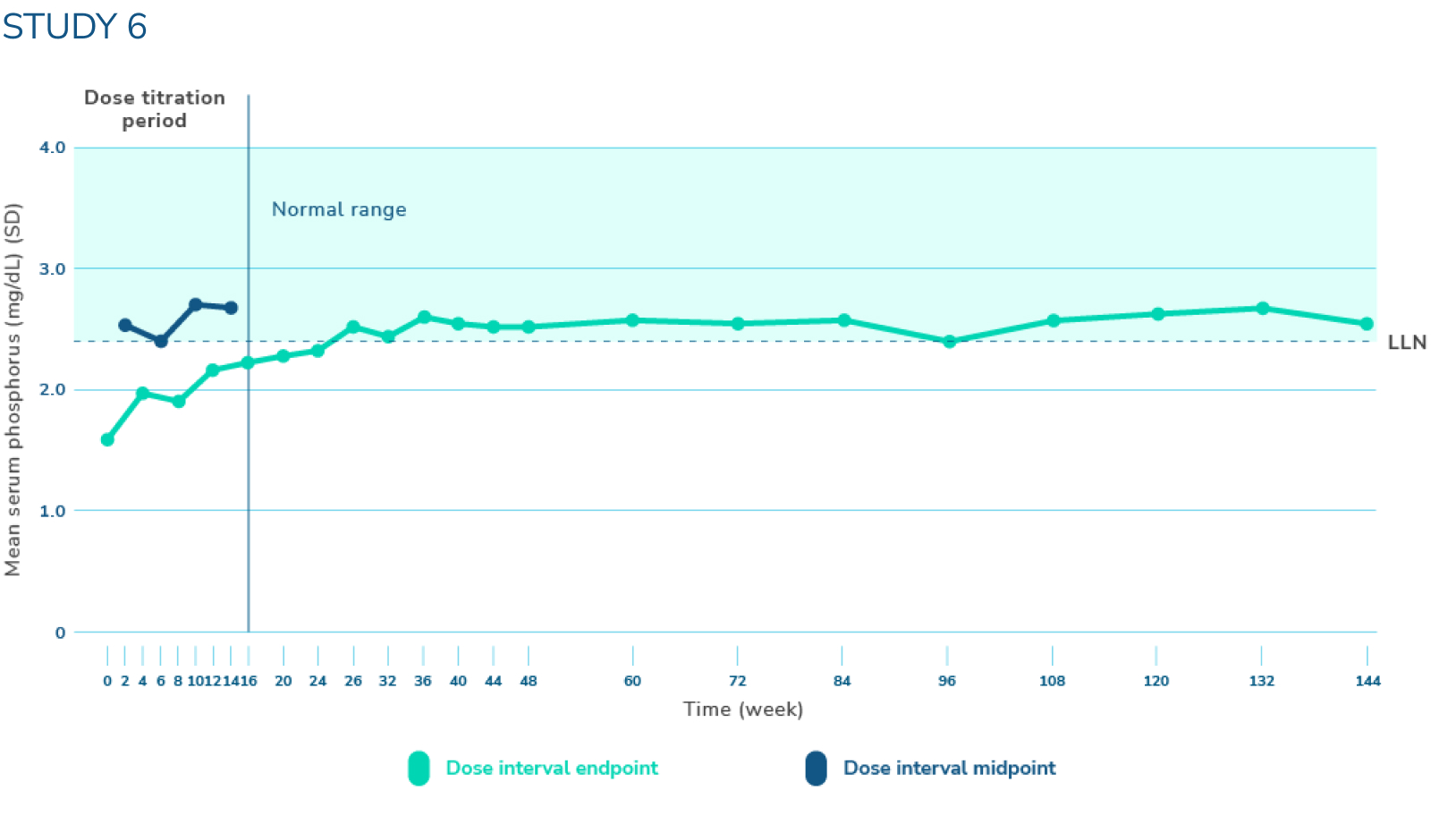
CRYSVITA increased and sustained mean serum phosphorus levels near or above the lower limit of normal1,3
*Serum phosphorus level (mg/dL) (mean ±SD). The dotted horizontal line represents the LLN (2.5 mg/dL). Normal levels of serum phosphorus range from 2.5 to 4.5 mg/dL. Note that the normal levels of serum phosphorus vary by age and sex, and ranges may vary by testing laboratory. At baseline, mean (SD) serum phosphorus levels were 1.60 (0.47) mg/dL. Mean (SD) serum phosphorus levels across midpoints of dose intervals (2 weeks post-dose) through week 24 were 2.64 (0.76) mg/dL with CRYSVITA.
LLN=lower limit of normal; SD=standard deviation.
In Study 6, across midpoints of dose intervals through week 24*:
- 50% (n=7) of patients achieved a mean serum phosphorus level above the LLN1,2
- There was an increase in mean (SD) serum phosphorus levels from 1.60 (0.47) mg/dL at baseline to 2.64 (0.76) mg/dL1
In Study 7, across midpoints of dose intervals through week 24*:
- 69% (n=9) of patients achieved mean serum phosphorus levels above the LLN1
- There was an increase in mean (SD) serum phosphorus levels from 1.62 (0.49) mg/dL at baseline to 2.63 (0.87) mg/dL1
STUDY 6
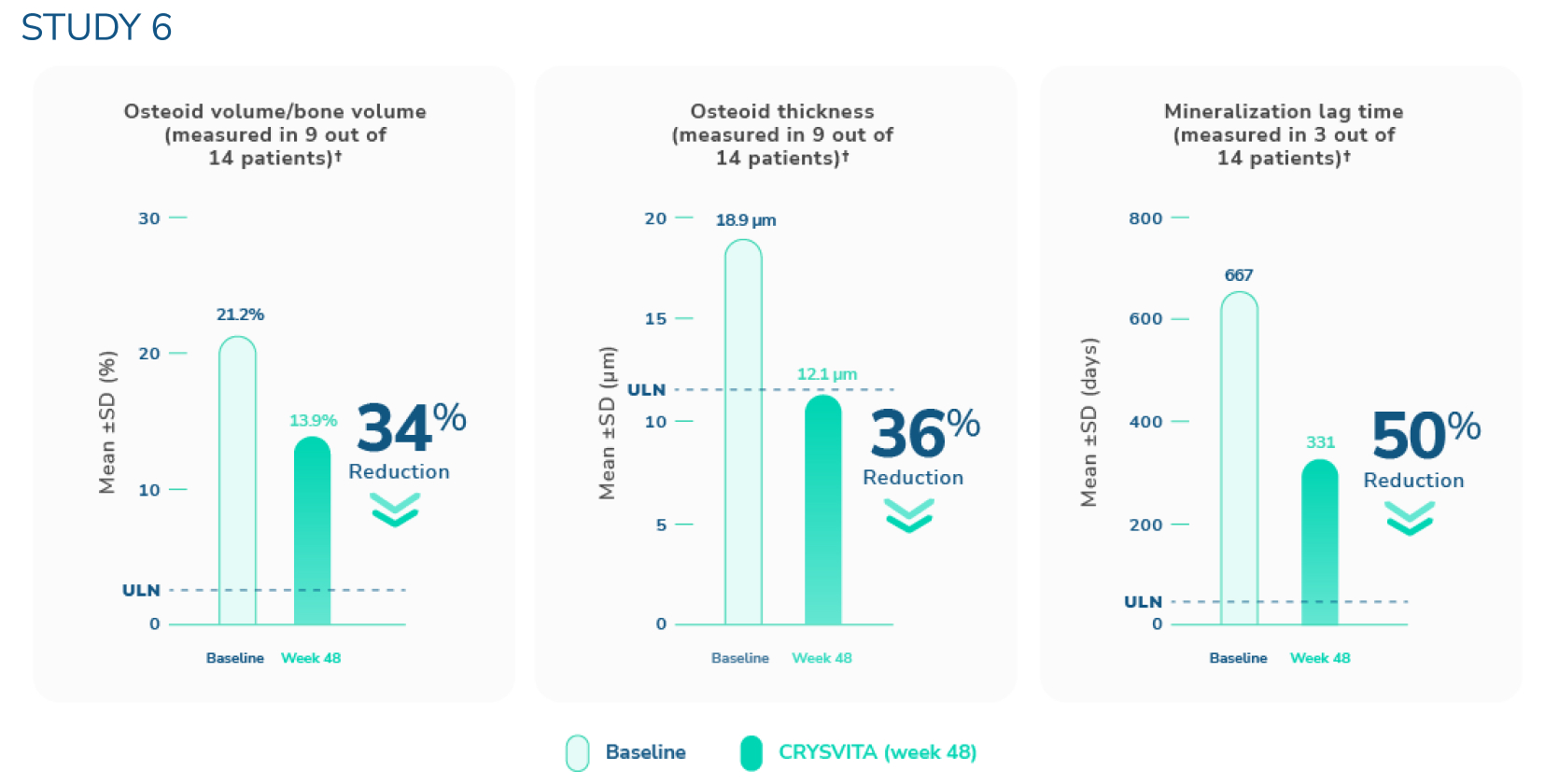
CRYSVITA helped heal osteomalacia1,3,6
†The upper limits of normal were defined as 3.05% for osteoid volume to bone volume, 8.9 μm for osteoid thickness, and mineralization lag time as 28.6 days.6
SD=standard deviation; ULN=upper limit of normal.
In Study 6 (N=14, ages 33 to 68 years), histological and histomorphometric assessments of iliac bone crest (biopsies) were examined for osteomalacia healing.1,3‡ CRYSVITA improved healing at week 48, with reductions in osteoid volume to bone volume (OV/BV), osteoid thickness (O.Th), and mineralization lag time (MLt).
In the 9 patients who presented with osteomalacia, the mean (SD) score decreased in OV/BV from 21.2% (19.9) at baseline to 13.9% (16.7), a 34% reduction. O.Th declined from a mean (SD) of 18.9 (11.9) µm to 12.1 (10.1) µm, a 36% reduction. MLt declined in 3 patients from a mean (SD) of 667 (414) days to 331 (396) days, a reduction of 50%.
‡Paired bone biopsies were performed in 11 of the 14 patients.
Osteomalacia and bone histomorphometry overview
Mineralization of the bone matrix (osteoid) is a critical step during bone formation. During this process, minerals are deposited to allow the “hardening” of the matrix into bone, hence the term mineralization.3,9
In Study 6, histological assessments of the iliac bone crest were used to determine the histomorphometric features of bone associated with osteomalacia.3,9
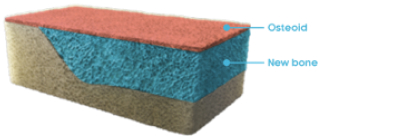
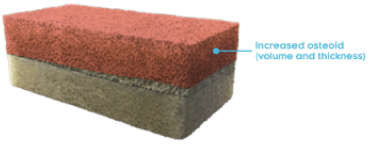
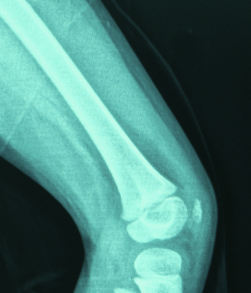
Bone matrix (normal)10,11

Normal bone12
Normal femur
In a normal bone:
- Osteoid volume to bone volume (OV/BV) ratio indicates the relative proportion of unmineralized bone matrix (osteoid) relative to mineralized bone13
- Osteoid thickness (O.Th) is a measurement of the width of mineralized bone matrix (osteoid)13
- Mineralization lag time (MLt) is the average interval of time between osteoid formation and osteoid mineralization13
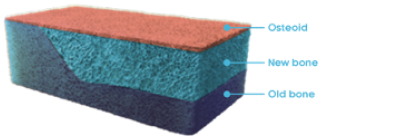
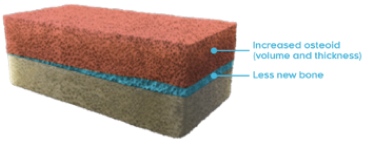
Bone matrix (osteomalacia)10,11

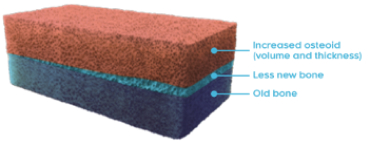
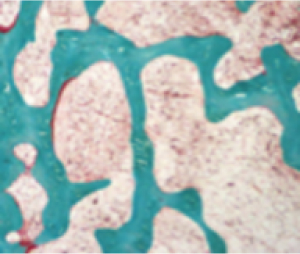
TIO (tumor-induced osteomalacia)12
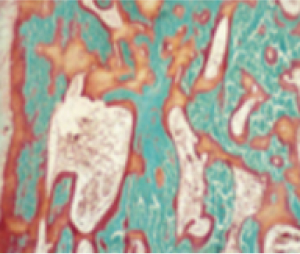
Pseudofracture
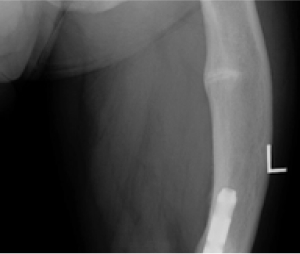
Osteomalacia is characterized by the following histomorphometric features4,14,15:
- Increased osteoid volume to bone volume
- Increased osteoid thickness
- Prolonged mineralization lag time
- Together, these indicate a greater presence of osteoid relative to mineralized bone, indicative of defective mineralization
STUDY 7
Study 7 also showed improvements in bone mineralization in patients treated with CRYSVITA1,4
At week 48 in 3 patients with paired bone biopsies, CRYSVITA healed osteomalacia, as demonstrated by bone histomorphometric assessments of osteomalacia, with a 34% reduction in OV/BV and a 16% reduction in O.Th.
STUDY 6
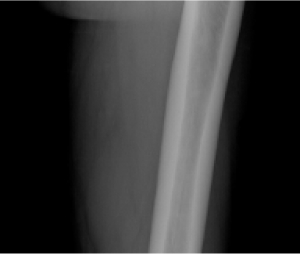
Radiographic evaluation of osteomalacia
CRYSVITA helped heal bone abnormalities as demonstrated by 99mtechnetium-labelled whole body bone scans. Scans were performed at baseline and subsequent timepoints during the study on all 14 patients. At baseline, 99mtechnetium-labelled bone scans detected 249 bone abnormalities across all patients in Study 6.1
CRYSVITA decreased areas of tracer uptake on bone scans from week 48 through week 144, suggesting healing of bone abnormalities.1
99mtechnetium-labelled whole-body scans use a radioactive tracer to identify areas of unusual bone rebuilding. In patients with TIO, increased tracer uptake on bone scans is presumed to be nontraumatic fractures and pseudofractures.1,7
Ready to start your patients on CRYSVITA?
Take the first step by filling out the enrollment form.